CATIE: A Space for Restoration
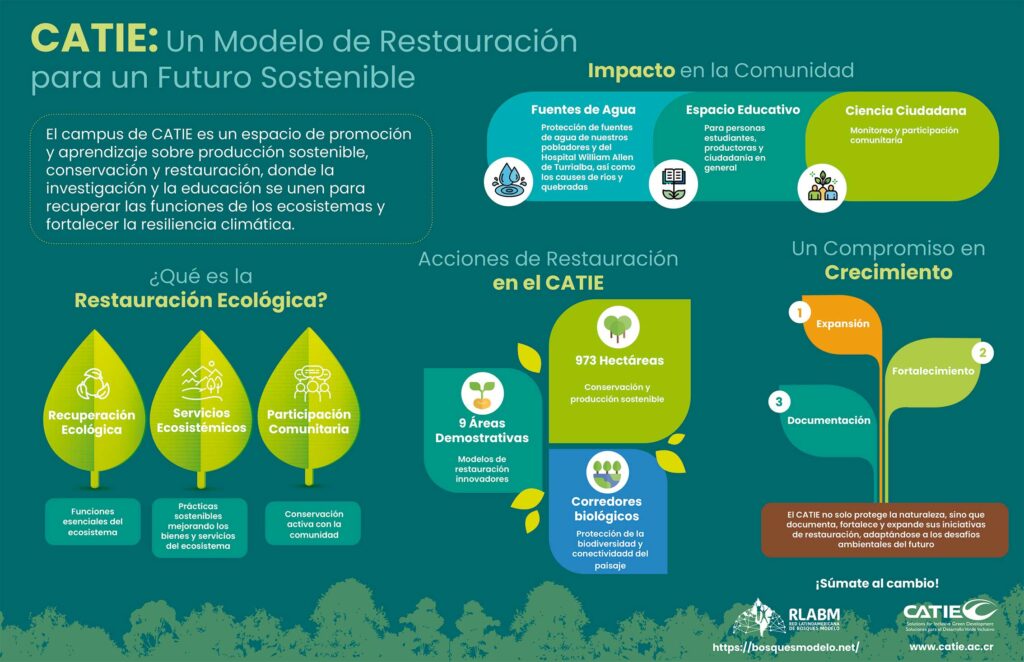
Environmental restoration not only involves the recovery of degraded ecosystems but also the enhancement of their ecological functions and the regeneration of ecosystem services that benefit both nature and communities. This process can encompass actions ranging from reforestation and soil rehabilitation to the reintroduction of native species and the mitigation of impacts caused by human activity.
Beyond an ecological action, restoration is also a social agreement that involves the active participation of local communities, ensuring its long-term sustainability and guaranteeing that environmental benefits are translated into well-being for society.
A Living Model of Restoration at CATIE
The CATIE campus is an example of applied restoration, conservation, and recovery of ecosystem services at the landscape level. With an area of 973 hectares, the campus has implemented demonstration areas dedicated to ecological and productive restoration.
Through assisted restoration, CATIE implements diverse strategies to mitigate environmental degradation, improve ecosystem resilience, and strengthen ecological connectivity within the biological corridor in which it is located.
Benefits of Restoration on Campus
Thanks to its restoration initiatives, CATIE has managed to recover and strengthen multiple essential ecosystem services, including:
- Protection of riparian corridors, contributing to water and biodiversity conservation.
- Ecological connectivity, allowing the movement of species and strengthening landscape resilience.
- Biodiversity conservation, creating suitable habitats for key species.
- Promotion of pollination, through the conservation of melliferous species and pollinator gardens.
- Scenic landscape restoration, fostering sustainable tourism and local economic development.
- Sustainable production, through agroforestry systems and forest plantations that contribute to carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
Research and Education for a Sustainable Future
The CATIE campus is not only a restoration space but also a center of innovation, where applied research, education, and demonstration models converge to drive sustainable solutions.
Through its integrated approach, CATIE continues to lead initiatives for landscape restoration, strengthen climate resilience, and promote production and conservation models that benefit both biodiversity and local communities.






